Canada held a National Summit on Combatting Auto Theft on February 8, 2024 in Ottawa. The Summit sought to bring together stakeholders to solve this very serious problem.
A major outcome of the Summit is that the government will disrupt the supply chain that makes available devices that are often used in vehicle theft by criminals in the process of stealing vehicles.
Vehicle theft has grown to be a very critical issue in Canada: The country is seeking to mitigate this situation. News reports reveal that car thieves have developed systematic techniques where it is easy to obtain stolen vehicles for sale in other markets. The federal government with the support of advocates is implementing plans to reduce this problem.
Should vehicle manufacturers do more to stop vehicle theft?
This very question of more remedies needed to stop vehicle theft has stimulated the growth of Aftermarket solutions. Antitheft systems and devices are growing in popularity becuase some people feel insecure about simply replying on the vehicle manufactures built-in security systems. The Forbes article below highlights this concern:
“Manufacturers are always working to improve the anti-theft measures in vehicles, but thieves work just as hard to defeat them. According to FBI statistics, in 2020 the U.S. saw an 11.8% increase in car thefts over the prior year, and the trend has continued. The National Insurance Crime Bureau (NICB) reported that over 1 million vehicles were stolen in 2022. That’s a 7% increase over 2021, and the first time there were over 1 million vehicles stolen since 2008.”
When the pickup truck was stolen, the thieves allegedly removed a factory-installed GPS tracker but the owner had his own backup plan: a second GPS tracker which was installed by a trained mechanic. This second telematics device enabled him to locate the Toyota Tundra at a parking lot in Toronto before he called the police.
The strategy of using a second backup tracker is a common strategy used all over the world: The typical weakness of this approach is Management and Maintenance. Management speaks to checking on the proper functioning of the Tracker at regular intervals. Maintenance requires prompt attention at the earliest signs of malfunction.
Information Risk
I believe that Information RISK is the typical reason why some persons chose backup security devices. Vehicle manufacturers adopt strategies to secure information on primary built-in tracking systems and devices so that vehicle security is not compromised. As the age old adage goes “a chain is as strong as its weakness link”.
The vehicle service and maintenance information systems has to be distributed downstream involving more human players which inherently increases the risk that ethical issues may compromise security. How to prevent Information from being leaked to bad actors is always a systemic concern.
Information Risk Mitigation
The Information Risk Management (IRM) plan addresses the risk mitigation strategy using policies, technology and procedures to minimize the probability of information security leaks.
Once it becomes apparent that vehicles are being stolen despite the IRM being in place, data should be collected and analyzed to assess how the IRM can be strengthened. The spectrum of compromises varies from sharing of Master Access Codes, Encryption Algorithms or an individual in the Supply Chain informing criminal elements how to defeat the built-in security.
The tools devices generally used to steal vehicles include GPS and GSM Jammers.
GSM & GPS Jammers
Information on how to temporarily block GSM and GPS Signal jammers are readily available online.
Tech-Savvy criminals can learn and become proficient
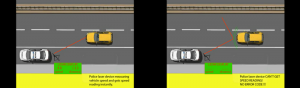
The GPS Tracker which is an Internet of Things (IoT) device, detects the attempts to jam GSM and GPS transmissions: This electronic attack interferes with the operation of the tracker in it’s function to protect the vehicle from being stolen. The small electronic circuit board within the device gathers GPS, GSM, Bluetooth data and other information that keeps the vehicle secure. Satellite data determines vehicle location and elevation.
Is the vehicle on a mountain road or driving through a tunnel under a river. The GSM module assists the GPS module by also providing tracking data based on Mobile Cellsite Towers: This information assists the GPS functionality of the tracker. The Mobile (GSM) data connectivity from the wireless telephone operators such as T-Mobile or Bell Mobility (Bell Canada) allows for the sending of Vehicle Tracking and Monitoring data from the Tracker to GPS Tracking platforms (Software) such as Navixy.com.